Comparative analysis of common PCR, real-time PCR and digital PCR
Ordinary PCR Basic Principle PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) is an in vitro DNA amplification technique that relies on DNA polymerase-based enzymatic reaction in the presence of template DNA, primers, and four deoxynucleotides. The amplified DNA fragment and its complementary oligonucleotide strand primers are subjected to multiple cycles of "high temperature denaturation - low temperature annealing - primer extension" in a three-step reaction, so that the number of DNA fragments increases exponentially in a short time. Get the large number of specific gene fragments we need. Semi-reserved replication of DNA is an important pathway for biological evolution and passage. PCR reaction system example 10× amplification buffer 10μl 4 dNTP mixtures 100~250μmol/L each Primer 5~20μmol/L each Template DNA 0.1~2μg Taq DNA polymerase 5~10U Mg2+ 1 to 3 mmol/L Add double or triple distilled water to 100μl Instruments and consumables The polymerase-based PCR instrument is actually a temperature-controlled device that is well controlled between denaturation temperature, refolding temperature and extension temperature. These instruments mainly use the variable temperature aluminum block, the variable temperature water bath and the variable temperature air flow to achieve the purpose of thermal cycling, each having its advantages and disadvantages, and will not be described herein. Result detection The PCR reaction amplifies a high copy number and the next step is critical. Fluorescein (EB, EB) stained gel electrophoresis is the most commonly used detection method. The detection specificity of electrophoresis is not too high, and non-specific hybrids such as primers and dimers are easy to cause misjudgment, but because of its simplicity and convenience, it has become the mainstream detection method. application PCR is a molecular biology technique used to amplify and amplify specific DNA fragments. It can be regarded as a special DNA replication in vitro. The biggest feature is the ability to increase the amount of DNA. Therefore, whether it is the ancient creatures in the fossils, the wreckage of historical figures, or the hair, skin or blood left by the murderer in the murder case decades ago, as long as a little bit of DNA can be isolated, it can be amplified by PCR. Correct. This is also the power of "trace evidence." Fundamental The qPCR technique involves adding a fluorescent reporter group and a fluorescence quenching group to the reaction system. As the PCR reaction progresses, the amplification product accumulates, resulting in the accumulation of fluorescent signals, thereby monitoring the entire PCR process in real time using changes in the fluorescent signal. Fluorescent labeling method method advantage Disadvantage Application range SYBR Green I Wide applicability Sensitive Convenience Cheap Primer requirements are high Non-specific bands Quantitative analysis of various target genes, research on gene expression, research on transgenic recombinant plants and animals in scientific research Taqman High specificity Good repeatability High price Only suitable for specific goals Pathogen detection, disease resistance gene research, drug efficacy assessment, genetic disease diagnosis Molecular beacon High specificity Low fluorescent background Only suitable for specific goals Design difficulty High price Specific genetic analysis, SNP analysis Fluorescent quantitative PCR reaction system example Reagent content 2xGoTaq Master Mix 5μl Nuclease-free water 3.5μl Upstream primer 0.25μl Downstream primer 0.25μl Genomic DNA 1 μl (about 20 ng) gradient dilution 10μl in total Instruments and consumables Adding a fluorescent signal acquisition system and a computer analysis processing system to the ordinary PCR instrument becomes a real-time PCR instrument. The principle of PCR amplification is the same as that of the common PCR instrument, except that the primers added during PCR amplification are labeled with isotopes, fluorescein, etc., and primers and fluorescent probes are used to simultaneously bind to the template for specific amplification. The results of the amplification are transmitted to the computer analysis and processing system through the real-time acquisition signal connection of the fluorescence signal acquisition system to obtain a quantized real-time result output. The PCR instrument is called a real-time PCR instrument (qPCR instrument). The real-time PCR instrument has single channel, dual channel, and multiple channels. When only one fluorescent probe is used, a single channel is used, and when there are multiple fluorescent labels, multiple channels are used. Single-channel can also detect multi-fluorescent labeled target gene expression products, because only one amplification of the target gene can be detected at a time, and multiple amplifications are required to detect the amount of different target gene fragments. The instrument is mainly used for medical clinical testing, biomedical research and development, food industry, research institutes and other institutions. Real-time PCR and normal PCR Real-time PCR Ordinary PCR Detection Fluorescence detection Electrophoresis running glue Specificity Primers and fluorescent probes with high specificity Primer, low specificity Sensitivity High sensitivity for fluorescence detection Electrophoretic detection is relatively low degree of automation No need to run glue, high degree of automation Run the glue after the end result Full monitoring, accurate algorithm for quantification Qualitative Pollution Closed system, less environmental pollution High possibility of pollution application Qualitative analysis studies: heterozygous or homozygous identification, SNP analysis, etc. Absolute quantitative studies: quantitative analysis of viruses and pathogens, quantitative analysis of gene copy numbers, quantitative detection by GMO, etc. Relative quantitative studies: mRNA expression analysis, siRNA effect confirmation, difference display results validation, etc. In 1992, Sykes et al. identified mutant leukemia cells from non-lymphocyte and normal somatic cell backgrounds and tested low-abundance IgH heavy chain mutant genes in complex backgrounds. Three important principles were proposed in this study: limited dilution, presence or absence of endpoint signals, and statistical processing of data Poisson distribution, which laid the foundation for the development of dPCR and gradually opened the curtain for Digital PCR research and application. ...... Tetanus Toxoid Vaccine,Toxoid Vaccine,Hep B Immune Globulin,Immunoglobulin Injections FOSHAN PHARMA CO., LTD. , https://www.foshanpharma.com
In 1985, Mullis et al. of PE-Cetus in the United States invented the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to simulate intracellular DNA replication in vitro. However, PCR with E-coli DNA polymerase makes this process time consuming, laborious, and error prone because of its heat resistance. In 1988, a thermostable DNA polymerase was extracted from a thermophilic aquaticus isolated from hot springs by Saiki et al. The application of the thermostable DNA polymerase enabled PCR to be carried out efficiently, and then PE-Cetus introduced the first PCR automated thermal cycler, which kicked off the PCR boom.
According to the development of PCR, this paper will analyze the three generations of PCR, such as ordinary PCR, real-time PCR and digital PCR. It is expected that readers interested in PCR will gain some benefits. 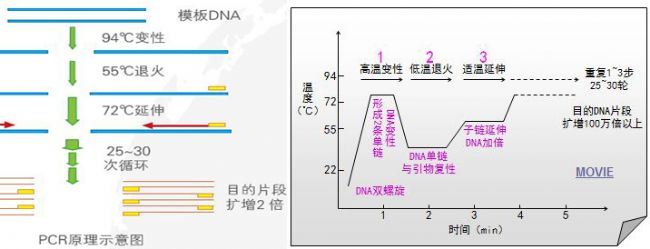
Real-time PCR (Quantitative Real-time PCR, qPCR) Â
According to the PCR quantitative principle formula, it can be deduced that the logarithm of the initial copy number of the template is linear with the number of threshold cycles. The more the initial copy number of the template, the fewer the number of cycles that the fluorescence signal reaches the threshold, that is, the smaller the Ct value. A standard curve is prepared using a standard sample of known starting copy number, and the fluorescence intensity emitted by the fluorophore is corresponding to the number of PCR amplification products. As long as the fluorescence signal is monitored in real time and the Ct value of the unknown sample is obtained, The initial copy number of the unknown sample is calculated from the standard curve.
The Ct value refers to the number of amplification cycles that the fluorescence signal of the amplified product passes through the set threshold when the PCR is amplified. The same template was used for 96 amplifications, and the amount of product at the end was not constant, but the Ct value was highly reproducible. 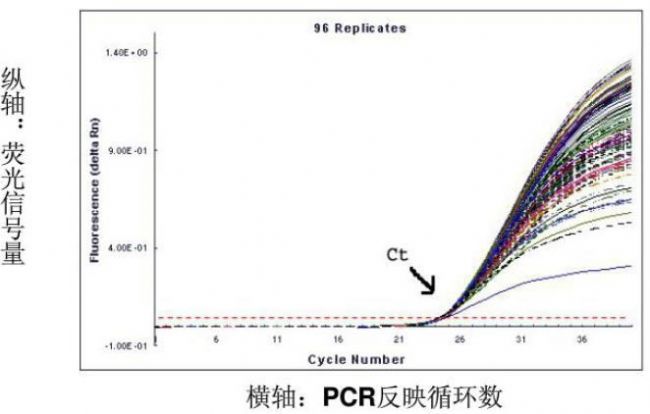
The more the amount of template DNA, the less the number of cycles the fluorescence reaches the domain value, ie the smaller the Ct value. The Log starting template concentration is linear with Ct. A standard curve can be made from a standard with a known starting copy number. Based on the sample Ct value, the amount of template contained in the sample can be calculated. 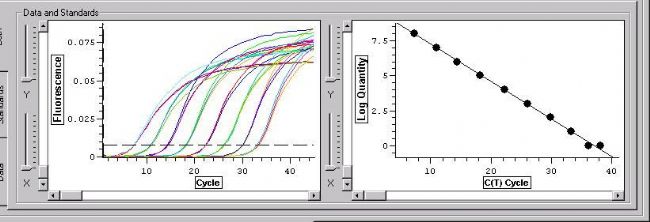


Three golden flowers, the first two, digital PCR (DPCR) next bloom!
references: