A Multiple Analytical Method for Antibody Screening of Cell Surface Receptors [Innovative Techniques]
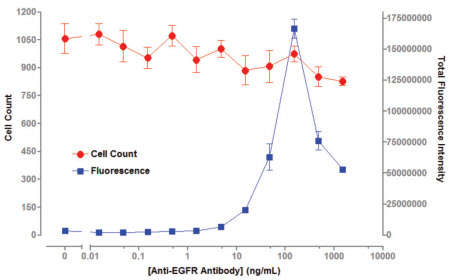
In this paper, the combination of human EGFR antibody and cell surface EGFR antigen is described as an example. The application of TTP Labtech's mirrorball instrument as a "mix-and-read" method in antibody screening is described. The protein family of EGFR ligands is involved in cell migration, adhesion and differentiation, and many diseases including breast cancer, lung cancer, and colon cancer are closely related to the overexpression of EGFR. The application of monoclonal antibodies to different target proteins is expanding and can be used for the treatment and diagnosis of different diseases (such as cancer, autoimmune diseases). Monoclonal antibodies are biological proteins secreted into cell culture media by specific cell lines for specific antigens, and high-throughput screening is an important component of antibody development. ELISA and Mix-and-read The use of conventional ELISA techniques has many limitations in antibody screening. Since ELISA technology relies on coated antigens on microplates, this method is not suitable for detecting low solubility antigens (such as cell surface receptors). Due to the mode of operation of the ELISA, it is difficult for the ELISA to screen for antibodies that recognize the native conformation of the cell surface antigen. Even for soluble antigen antibody screening, the adsorption of the antibody by the microplates changes the conformation of the protein, which in turn does not recognize antigen-specific epitopes. A "mix-and-read" analytical method is widely used in the field of monoclonal antibody screening in the biopharmaceutical industry. This "mix-and-read" analysis method involves adding all of the assay components to a well and then incubating to bring the bonds to equilibrium. For antibody screening, the method can be assayed using antigen-coated beads or antigen-expressing cells, and antigen-antibody interactions can be detected by fluorescence intensity of fluorescently labeled conjugates bound to beads or cells. The bound fluorescence can be analyzed using a cell technology instrument without washing to distinguish between bound and free fluorescence in the test well. In the invention of FMAT, Lee et al. detailed the advantages of the traditional ELISA method cell counter. Compared with the traditional ELISA analysis method, using this technology to analyze the "mix-and-read" experiment can improve the sensitivity of the detection and the throughput of the analysis, and also improve the identification and detection of antibodies. High speed multiplex analysis TTP LabTech's mirrorball is well suited for this "mix-and-read" assay, and because of its high sensitivity, it can detect low-abundance expressed cell membrane proteins. The instrument not only enables single laser scanning, but also 405, 488, 640nm laser scanning at the same time, so you can choose a variety of fluorescein. It can be independent of the ability of the excitation light to directly correct the emitted fluorescence, allowing for multiple analysis of beads and cells in antibody screening applications. In this article, human EGFR antibody is combined with cell surface EGFR antigen as an example to describe the application of TTP Labtech's mirrorball instrument as a "mix-and-read" method in antibody screening. The protein family of EGFR ligands is involved in cell migration, adhesion and differentiation, and many diseases including breast cancer, lung cancer, and colon cancer are closely related to the overexpression of EGFR, thus inhibiting the expression and activation of EGFR. It plays a very important role in the treatment of these diseases. To detect the sensitivity of mirrorball detection, the communication used two epithelial cancer cell lines A549 and A431, which highly express EGFR, to analyze the binding capacity of different concentrations of anti-EGFR receptor to EGFR. The conventional screening method uses the ability of cells expressing and not expressing antigen to perform antibody binding, respectively, to achieve antigen-specific antibodies, such as cells transfected with the gene of interest and host cells that have not been transfected for reverse screening. If an existing screening platform (eg, ELISA and FMAT) is utilized, two plates need to be prepared to compare the binding ability of the antibody to the two cells to determine antigen-specific binding ability. In this experiment, mirrorball can measure the antibody binding ability of various cells in a cell microplate to distinguish the specific binding of antibodies to different cells. This diversified analytical capability of mirrorball can greatly reduce the throughput of the experiment while increasing the throughput of the screening and eliminating the differences between the microplates. experimental method Cell line and cell culture This article compares A549 and A431 cells expressing the EGFR receptor, A549, A431 and Jurkat cells were purchased from Sigma. The culture conditions of the three cells were as follows: A549 cells: DMEM containing 10% FBS, 2 mM L-glutamine and 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 U/ml streptomycin; A431 cells: EBSS (Sigma) containing 10% FBS, 2 mM glutamine , 1×Non-essential Amino Acids (NEAA) (Sigma), 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 U/ml streptomycin; Jurkat cells: RMPI-1640 (Sigma), 10% FBS, 100 U/ml penicillin, 100 U/ml chain Mycin. A431 and A549 cells were cultured to a density of 80%, digested with 0.25% trypsin and EDTA, washed, and resuspended in new medium. Unlabeled culture reagents were obtained from Life Technologies. Mouse anti-human EGFR antibody was purchased from Merck Chemical Company (#GR01). Goat anti-mouse IgG, AlexaFluor 647 detection marker (#A21235) from Life Technolgy. CSFE and BiO mark 5(6)-Carboxyfluorescein diacetate N-succinimidyl ester CFSE (sigma) was dissolved in DMSO to give a CSFE concentration of 100 mM. 10 nM CSFE was added to the cells, incubated for 10 minutes at room temperature, then the incubation was stopped by the addition of 4% PBS (2 ml) and incubated for 10 minutes at 37 °C. The cells were washed and centrifuged at 1000 x g for 5 minutes. For cell count analysis, 30 nM of DiO (Life Technology) was added to the assay mixture and incubated overnight. After the cells were labeled, they were excited by a laser at 488 nm, and the fluorescence signal of the cells was detected in the FL-1 channel. The anti-EGFR antibody was serially diluted in the cell culture medium, and 20 ul of the diluted antibody at different concentrations was added to a 384-well microplate (Costar 3712). A mixture containing 1.25 x 105 cells/ml of suspension cells (A431 or A549) and 6 nM anti-mouse IgG AlexaFluor 647 marker was prepared. 20 ul of the cell suspension was separately added to the microplate containing the antibody, and then the plate was incubated overnight at 37 °C. The microplate was tested at mirrorball to determine the amount of anti-EGFR bound to the cells. Cell multiplex assay 20 ul of diluted different concentrations of anti-EGFR antibodies were added to 384 microwell plates. EGFR+A549 and CSFE-labeled EGFR-Jurkat cell suspensions containing the same number of cells (total cells 1.25 x 105 cells/ml, 6 nM anti-mouse IgG AlexaFluor 647 marker) were prepared. In this experiment, 20 ul of the cell suspension was added to a microplate containing 20 ul of anti-EGFR antibody (the number of cells in the well was 2.5 x 103 cells and 3 nM detection label). After incubating the microplates at 37 ° C overnight, the fluorescence intensity of the CSFE dye and the bound antibody was detected by simultaneous scanning in a mirrorball using a 488 nm and 640 nm laser. Mirrorball data collection and scanning The samples were scanned using a 488 nm and 640 nm laser on a mirrorball. Objects in each well can be in-situ analyzed using TTP Labtech's patented threshold calculations, while providing morphological and fluorescence parameters. The data can be displayed in a variety of ways using mirrorball's unique Cellista software, including histograms, scatter plots, 3D fluorescence intensity maps, and images of the entire hole. result Detection sensitivity of EGFR's Mix-and-read analysis In this study, in order to assess the sensitivity of the assay in cell-level binding assays, A431 and A549 cells, different concentrations of EGFR antibody and Alexa Fluor 647-labeled goat anti-mouse IgG were incubated overnight. Figure 1 shows that the detection concentration of EGFR antibody on A431 cells is 5 ng/ml, while the detection limit on A549 cells is 5-10 ng/ml. This indicates that the expression level of EGFR on A549 cells is lower than that of A431 cells. This result indicates that the level of anti-EGFR antibody detected by mirrorball is consistent with the results of FMAT that has withdrawn from the market. Both assays showed a decrease in total fluorescence intensity at antibody concentrations above 100 ng/ml, a phenomenon that was due to the "hook effect" in the literature. Due to the excessive presence of the primary antibody, the fluorescence bound to the detection antibody cannot be read. Figure 1. Total fluorescence intensity on A431/A549 is enhanced with increasing anti-EGFR antibody concentration. Multiple laser scanning The mirrorball's three lasers allow users to perform cytometric analysis using a variety of fluorescently labeled markers. In this study, A549 cells were labeled with DiO (excitation at 488 nm laser) and multiple analyses were performed using EGFR antibodies and AlexaFluor 647 markers. After overnight incubation, cell number and EGFR marker analysis were performed using dual lasers at 488 nm and 640 nm. Figure 2 shows that in the case of a constant number of cells, the total fluorescence intensity of the cells is increased with increasing EGFR antibody concentration. A very important feature, the number of cells can be obtained without the binding of EGFR antibodies. Figure 2: Total fluorescence intensity of A549 cells is enhanced with increasing EGFR concentration, and cell counts can be read separately. Multiple analysis of cells The multiple laser scanning features unique to mirrorball distinguish cell populations from expressed and unexpressed cells in transfected and host mixed cells. To elucidate the characteristics of this aspect, binding assays for EGFR antibodies were performed in A549 (EGFR+) and CSFE-labeled Jurkat (EGFR-). Jurkat cells were stained for CSFE (10 nM) prior to analysis. Figure 3 shows a 3D fluorescence intensity spectrum of A549 and Jurkat cells under binding conditions of 100 ng/ml antibody. It can be seen that EGFR antibody specifically binds to A549 cells, and binding of EGFR antibodies is not detected in Jurkat cells. Figure 3: Three-dimensional analysis of cell counts. In mixed cells, mirrorball uses multiple laser scans to simultaneously detect fluorescence signals from A549 and Jurkat cells. Figure 4 shows that EGFR antibody binding experiments were performed using A549 single cells and A549, Jurkat mixed cells, and there was no significant difference in detection sensitivity. Figure 4: Comparison of EGFR binding experiments using single A549 cells and Jurkat, A549 cells. There was no significant difference in binding experiments using single cell populations and mixed cells. discuss TTP Labtech's mirrorball microplate reader provides a robust, read-and-read approach to screening for cell surface antigen antibodies. The instrument is ideal for the development of antibodies, and its unique optical components and software design make the instrument extremely sensitive to detection, enough to detect low-abundance protein binding experiments. This article shows that the EGFR experimental design is very simple and can be analyzed on a mirrorball with a simple modification. This "Mix-and-read" analytical method eliminates the need for washing and incubation steps compared to conventional ELISA steps, thereby greatly reducing the time required for screening. At the same time, the experiment uses less sample and reagent consumption, resulting in significant savings in the cost of the experiment. The mirrorball is the first generation of analysis systems that provide simultaneous scanning of multiple lasers, which can be used to correct fluorescence between lasers. Used in combination with suitable fluorescent reagents, this multi-laser simultaneous scanning capability enables independent cell identification and multi-parameter analysis, providing screening throughput, greatly reducing the cost of the experiment, and making the experimental procedure very convenient. In this article, with the counter-staining of DiO, the number of cells can be directly determined independently of the binding of antibodies, thus eliminating false positives due to differences in cell vaccination or cytotoxicity. In addition, mirrorball has the ability to distinguish between host cells and cells transfected with specific genes in the same well, which greatly accelerates the process of antibody screening. Mirrorball also has the ability to simultaneously detect A431 and Jurkat cells in the same well. Multiple analysis of cells has many advantages, such as the exclusion of plate-to-plate differences between different cells, double the screening flux, and reduce sample usage. references For more information, please visit the mirrorball product information. Surgical Instruments Kit,Disposable Surgical Kit,Hospital Surgery Surgical Kits,Disposable Sterile Surgical Kit Henan Xianghe Medical Materials Co., Ltd. , https://www.xiangheweicai.com
Antibodies and reagents
EGFR experimental design 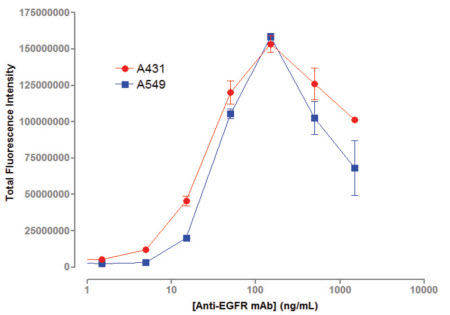


1. Lee, R., Tran, M., Nocerini, M. and Liang, M. (2008) A High-Throughput Hybridoma Selcetion Methods Using Fluorometric Microvolume Assay technology. J. Biomol. Screening 13: pp210-17.
2. Bowen, W. and Wiley, P. (2006) Application of Laser-Scanning Fluorescence Microplate Cytometry in High Content Screening. Assay and Drug Development Technologies. 4: pp209-2