Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study on Micropore Pore Structure of Coal Reservoirs
Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study on Micropore Pore Structure of Coal Reservoirs Coalbed methane mainly exists in coal pores in the state of adsorption. Correct understanding of the pore structure and distribution characteristics of coal is an important basis for studying the porosity, spatial structure, seepage characteristics and coalbed methane recoverability of coal reservoirs. At present, the pore structure and pore size distribution characteristics of rock are mainly evaluated and analyzed by capillary pressure curve obtained by mercury intrusion method and adsorption desorption curve obtained by low temperature nitrogen adsorption desorption experiment. In view of the fact that coal reservoirs are characterized by fragility, compressibility, pore structure complexity and high heterogeneity compared with conventional reservoirs, this makes the two methods have many disadvantages in coal reservoir application. For example, the low-temperature nitrogen adsorption desorption experimental method for the sample pore size test range of 1. 7 ~ 300 nm, can better reflect the distribution of micro-holes and mesopores, but can not reflect the distribution of macro-holes and fractures, the test range has Limitations; mercury intrusion method is harmful to the sample, and can not be reused. Low-field NMR technology test principle is different from the above two methods, mainly by measuring the T2 relaxation time of the fluid in the pores of coal rock to obtain tiny in the coal sample pore system. Distribution of pores, mesopores, macropores and fissures, connectivity, and various physical parameters of coal and rock. The method has the advantages of fast, non-destructive, rich information and the like. Low field NMR experiment results Relationship between nitrogen absorption/desorption curve characteristics and surface relaxation rate of coal sample liquid For more details, please refer to the literature “Low-field NMR study of pore structure of micro-pores in coal reservoirsâ€. Journal of Coal Science 40th Supplement 1 June 2015 June 2015 Feed Additives,Tocopherol For Feed Additive,Animal Feed Additive,Feed Additive Vitamin E Allied Extracts Solutions , https://www.alliedadditives.com
The T2 relaxation time spectrum of the coal sample was obtained by low field nuclear magnetic resonance experiments (Fig. 3). According to the morphological characteristics of the sample T2 spectrum, the samples are mainly divided into two types according to the pore size: one type of micropores is dominant, the mesopores, macropores and fissures are not developed, such as high coal rank samples; another type of sample micropores Large pores or fissures are dominant, and mesopores are relatively undeveloped, such as medium coal samples. 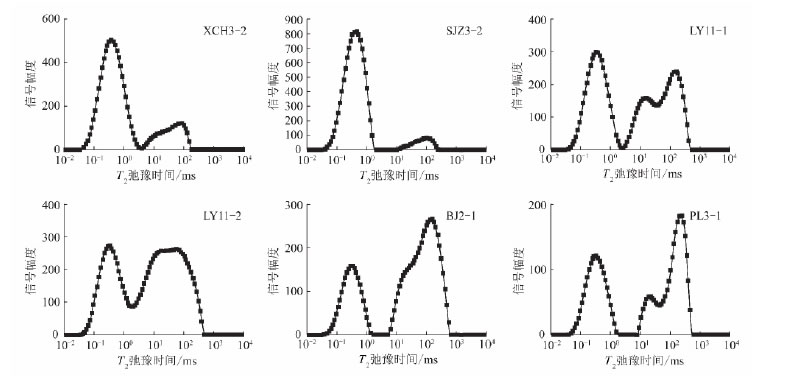
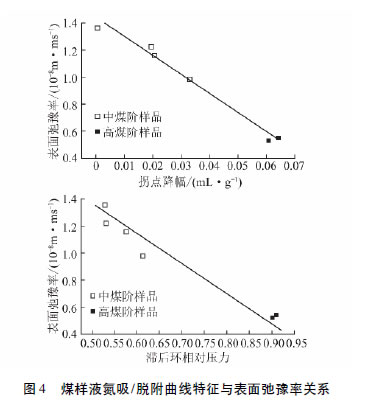
The surface relaxation rate of high coal rank coal is obviously lower than that of medium coal rank coal. The main reasons are as follows: The high coal rank coal has a relatively high proportion of micropores, the pore structure is more complicated, and the “fine flask†type capillary pores are mostly the Lord. Therefore, the surface relaxation rate has a good correspondence with the complexity of the pore structure of the sample and the pore type.