A comprehensive understanding of the key points of genetic testing entering the consumer market
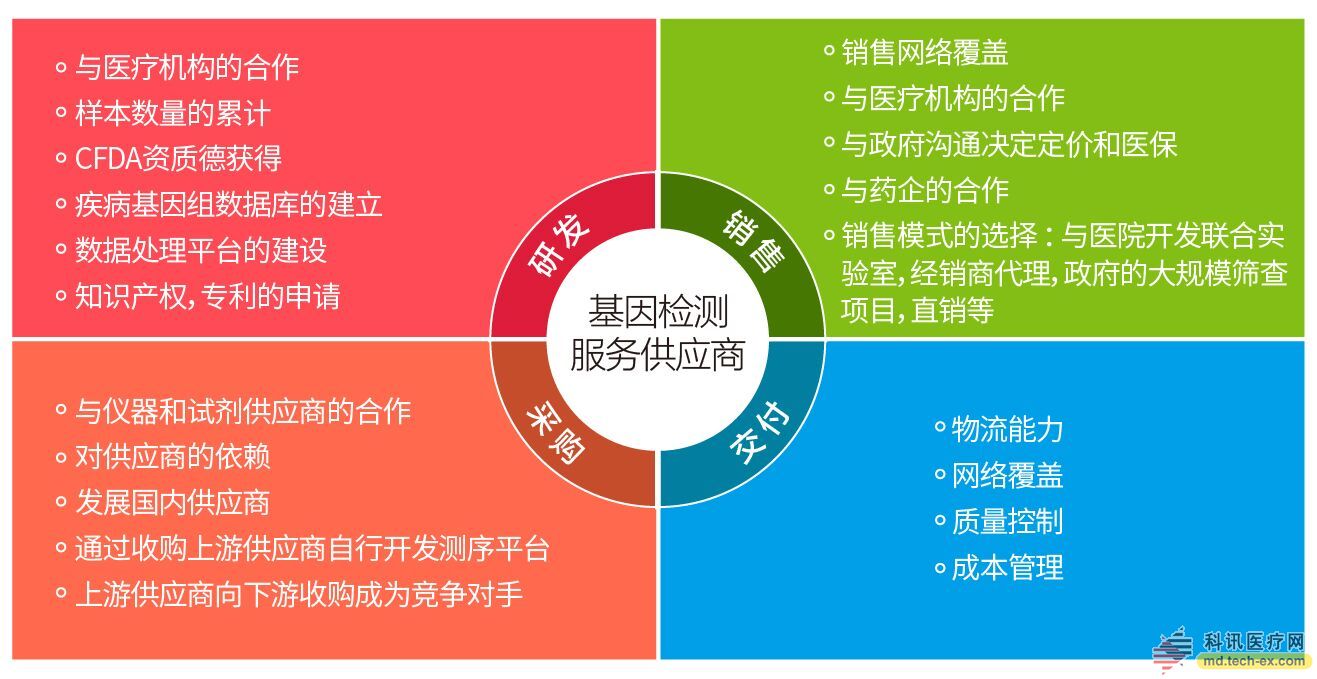
Release date: 2015-02-28 At present, more and more media are beginning to re-hype genetic testing, and many people feel that consumption and capital markets are paying more and more attention to genetic testing. Is it true that the spring of the genetic testing market has arrived? Can genetic testing become a necessity after this wave of enthusiasm? Below I will discuss the key turning points of genetic testing as a necessity from the bottleneck of genetic testing, model innovation and data interpretation. The three major bottlenecks of genetic testing affect the heat of the consumer market There are three major problems that genetic testing needs to solve in order to truly enter the consumer market. The first is price opacity. 23andMe spent 10 years reducing the price of genetic testing from $999 to $99. Each financing brought a new round of price cuts, and $99 was also introduced after its fourth round of financing. Before the price cut, their number of users was 180,000. After a short price reduction of nine months, the number of users has doubled. 23andMe realized the price of 99 dollars for genetic testing When the price of genetic testing abroad has been standardized, the domestic genetic testing market has appeared chaotic. In Baidu search, you can see a lot of genetic testing companies, pick up the phone and ask, the price ranges from several hundred thousand to several hundred. The domestic genetic testing market has always been in the gray sales area. On the one hand, because of the uncertainty of the relevant department's control policies, which one is not willing to be the star of the bird; on the other hand, it is because the gene company is not transparent about the pricing of genetic testing products. In the eyes of consumers, the pricing of genetic testing is opaque, and because consumers lack basic knowledge about genes, they are at a disadvantage of information asymmetry in the process of purchasing. In the hospital, you can only passively accept the doctor's recommended price, and you are also skeptical at the medical examination center, not to mention the possibility of picking up the goods. Pricing is a shackle that can't go through. While holding the legs of the service provider, while holding the hearts of consumers. The opaque pricing of technology providers has forced service providers to push prices up extremely; information asymmetry and low scientific popularity have led consumers to even associate genetic testing with constellation fortune telling. Second, there is still a huge gap between the time period of gene sequencing and a good user experience. A recent article is a bit of a fire, telling how a biological specimen started its "travel" until a genetic test was completed. It should be pointed out that the entire "journey" of this "biological specimen" took only two weeks. From transportation to laboratory to analysis room to final inspection report, the whole process was very "high". The article did not point out that the journey of this “biological specimen classmate†was the application of the drug guidance in gene testing. This kind of genetic testing is aimed at patients who have cancer, so do genetic tests need to be done for ordinary healthy people? To answer this question, it is necessary to start with the genetic testing of disease risk predictions for healthy people on the market today. Oxford Nanopore's small sequencer that produces genetic data for hours Genetic testing for disease risk in the general market requires only a few hundred dollars and a cotton swab with your saliva to analyze the health risks of at least one disease. This risk analysis can be done through the genetic information of certain disease susceptibility genes, with the fastest cycle of the entire week and the slowest month. There is a user experience problem here. If you want to experience a nail, the manicurist can serve directly, but the genetic test can't report the results on the spot! Many consumers may think that when they first hear the product of genetic testing, they think that they can produce the same results as blood glucose or blood pressure, or at least wait a few hours. Unfortunately, the little friends were disappointed. The cost of gene sequencing is currently down, but the entire genetic testing cycle is still not very close. Even if the sequencer can be carried into the home of the people in the future, the pre-sequencing DNA extraction, sequencing sample preparation, and later data analysis are all difficult to do foolish operations. From the current enthusiasm for wearable devices on the market, perhaps in the near future, the development of the sequencer can move toward the wearable direction. The ever-changing new technology is also the driving force behind the continuous decline in the price of genetic testing and the gradual shortening of the cycle. Illumina has implemented a $1,000 genome sequencing with HiSeq X Ten, and the new genomic analysis chip "Japonica Array" takes less than a week to complete genetic testing. Perhaps the advancement of commercialization can make these two bottlenecks find a balance point acceptable to consumers in the market. Third, the third bottleneck in gene sequencing is data analysis. As a technical man who is born out of biological information, the author may laugh when he sees this bottleneck. How can the bottleneck of genetic testing be data analysis? Indeed, it can be seen from the white paper published by 23andMe that the data analysis techniques used in genetic testing are not difficult. I don't mention the genetic testing of the first-generation sequencing technology (PCR sequencing). Interested readers can directly see our Qiyun Nord platform. The genetic testing of this generation of sequencing technology is currently a few minutes. Fully automated report generation process); Gene detection of chip technology From data analysis to report generation, basically a laptop can be fixed (experienced readers can use the R language package PredictABEL to do a complete set of data analysis) Second-generation sequencing technology for genetic testing, currently using the Churchill algorithm for genome-wide sequencing data analysis, which is a laptop three hours of work. Can it be said that this bottleneck does not exist? Of course not. Imagine that people who really understand biological information, who really understand the application of algorithm analysis and interpretation of genetic data, really know how to model and optimize the process of genetic testing analysis. In the field of genetic testing, the bottleneck is no longer a cost, but an explanation of the results. The reason why this bottleneck is proposed is not the difficulty of analyzing the technology, but the difficulty of selecting the above results. This is also the difference between each genetic testing company in each testing project. In this series, "Can you understand the genetic testing report?", I will examine this technical bottleneck in detail. The business model of genetic testing remains to be innovated Start with a very simple sentence: Can genetic testing products make money? Let's review the history of genetic testing technology transformation. In 1994, we took the lead in screening for colorectal cancer genes in US medical institutions. A year later, the UK began a comprehensive genetic screening system. In 2002, more than 700,000 people in the European Union conducted genetic testing. In 2004, the World Health Organization launched an international standard for genetic testing. In the same year, more than 5 million people in the United States received genetic testing. Genetic testing has become a standardized clinical test for medical institutions. In 2006, the Internet giant brought genetic testing into the lives of ordinary people. Google’s investment in 23andMe was established. In 2007, genetic testing companies began to take root in countries around the world. In the country, genetic testing companies such as “Joint Gene†began to appear. By 2008, Time Weekly will Personal genetic testing services were named the best invention of the year. From the perspective of the transformation of traditional genetic testing technology, the conventional model is to carry out clinical disease gene detection. When genetic testing is applied in the medical field, the target target is a sick consumer, but it is still a doctor who really needs to purchase genetic testing. Here is the model of “wool out of the dogâ€. This market includes monogenic disease detection, tumor personalized treatment testing, hereditary tumor prediction testing, early tumor screening. From the point of view of genetic testing, assisted reproduction and prenatal genetic testing of pregnant women are products with strong market demand, and are also the “cakes†that major medical institutions compete for. These products must be the focus of national policy norms, and the models are basically The above is "the wool is on the sheep." In addition, between the above two modes, there are some non-critical genetic testing products, such as neonatal genetic testing, adult genetic testing, and genetic testing for the elderly, which are gradually being introduced to the market by the Internet model. The bottleneck in the pricing and reporting of genetic testing mentioned above is a breakthrough in model innovation. The Health Planning Commission and the National Development and Reform Commission have made qualification restrictions on some of the genetic testing products currently on the market, and there are no further moves in terms of market pricing and approval of project standards. The price of genetic testing products on the market is ranging from thousands of dollars to 10,000 yuan. The chaos of pricing and the lack of reasonable interpretation of information are the flaws in the model of genetic testing that cannot be broken. The author estimates that this contradiction will begin to erupt in 2015. During the period, the capital market and the genetic industry will have a process of shuffling. The final part of this series will analyze in detail which industries will be subverted. Business model for genetic testing There is still a distance between the genetic testing product and the consumer's pain point. Consumers need to address pain points, and if they only ask questions, consumers cannot treat them as necessities. At present, there is a big threshold for genetic testing products. Is the final interpretation report helping consumers solve their problems? R&D personnel who are genetic products will always ask: What problems do consumers need to solve with genetic testing reports? This is an infinite loop of genetic testing products in the Chinese market. On the one hand, the terminal consumer cannot understand the value of the report, and on the other hand, the testing service provider cannot know the true pain point of the user. Perhaps a third-party service company will be born here, and that is the provider of genetic testing reports. To have such a business, one problem needs to be solved: to enable consumers to read the genetic test report. Before such a company has yet to appear, let's take a look at how the ordinary people will see the report after they get a genetic test report. Genetic testing can be divided into diagnostic and preventive categories in simple terms. Diagnostic gene detection reports include genetic defect gene detection, non-invasive prenatal genetic testing, and targeted drug gene detection. Prevention categories include disease susceptibility gene risk assessment, neonatal genetic testing, and the like. For the genetic testing of diagnostics, it has always been a "cake" for the major medical institutions and enterprises in the market. A diagnostic gene test report can't be interpreted by ordinary people. It needs a professional medical institution genetic counselor or a qualified doctor to interpret it. For example, targeted drug gene detection reports, many drug names and related gene function descriptions, as well as applicability, inapplicability, possible applicability, etc., need to be interpreted by consultants and physicians with professional clinical medical background. Make a proper diagnosis. This kind of diagnostic gene detection report, national related policy restrictions will also be introduced, such as CFDA for diagnostic equipment, the Health and Welfare Commission for diagnostic projects, etc., not only that, the author predicts that the relevant departments will also diagnose the gene The test report is standardized and standardized, and the clinical diagnostic guidance brought by the report will further introduce technical specifications. The genetic testing of diagnostics is risky, but it can be guaranteed by medical institutions and insurance companies under the regulations of relevant national departments. For the prevention of genetic testing, if you tell the ordinary people, if you know that the disease can not be cured, consumers are really willing to know the risk of suffering from a certain disease? For newborn genetic testing, although babies can't make decisions about their own genetic testing, parents choose to know if the information is really good and harmless. If we leave the current genetic testing accuracy and qualification issues, just look at the prevention gene detection report, you will find that more testing projects are divided into two directions: one is to prepare consumers for the transition to diagnostic genetic testing, For example, the cancer susceptibility gene detection package, the consumer knows only a "not very stable" (why is called less stable, the author does not elaborate here, will slowly analyze the technical details of genetic testing, in short, consumption The statistical probability that the results obtained by different genetic testing companies will vary. The other direction is to attract consumers to make one-time consumption through games and curiosity. Here is a story that attracts Internet investors, that is, “first enter the user circle, then profit through value-added services, and finally use the gradually accumulated Big data to build the threshold. This beautiful business model has indeed saved a lot of money for many investors, but the results remain to be seen. Genetic testing for prevention is risky, but it is up to the consumer to know the problems that arise after the risk. All in all, the report of genetic testing, the people can not be interpreted and applied (diagnostic genetic testing), or satisfied with curiosity and then "sold" to the traditional health care industry (preventive genetic testing). It is full of all kinds of "pits". Genetic testing can really help us solve some of the pain points, but the road ahead is long. In addition to using investors' money to fill the "pit", the experts in the genetic world, we Shouldn't you calm down (don't just think about making money from investors), focus on analyzing consumer pain points, improve user experience, and let products and markets talk? Which industries will be deeply integrated with genetic testing in the future? As one of the most cutting-edge new technologies, genetic testing has been recognized by more and more industries. From the perspective of the stability and accuracy of current genetic testing technology, the market needs a certain period of integration. 2015 is a crucial year for the marketing of genetic testing. With the supervision and regulation of genetic testing by relevant national departments, the application of genetic testing will continue to accelerate. Below we analyze several large industries one by one. First, the clinical diagnosis industry US President Barack Obama announced the "Precision Medicine Initiative" in his 2015 State of the Union address, and proposed that the country invest 215 million in the "Million Genome Project." This plan is another era in which the United States has once again brought human medicine into a new era following the Human Genome Project. This new era marks the beginning of genetic testing as an important criterion for clinical diagnosis. The goal of precision medicine is to create the optimal treatment for each patient, maximizing efficacy and minimizing side effects. To achieve this goal, we need to look for the cause from a molecular perspective. In simple terms, we need to perform genetic testing on everyone. The US investment in precision medicine is just the tip of the iceberg of genetic testing to subvert the clinical diagnosis industry. For the genetic industry, this opportunity is more like a sign before the typhoon. Second, the drug development industry Another direction of “precise medicine†is “precise medicineâ€, which aims to provide patients with the most favorable treatment. The development of new and effective drugs not only costs huge amounts of money from the state and enterprises, but also faces many problems, such as the increasing number of people targeted by drugs and the longer and longer drug development cycles. Here, it is necessary to accumulate more data through genetic testing to achieve accurate drug development and to understand the cause at the genetic level. Third, the health prevention industry Precision Medicine has created a vast library of patient medical data. This huge resource library allows clinical data to be “tracked†and to make the root cause of the disease “availableâ€. Researchers can study these data to further understand the underlying causes of the disease and propose more rational and comprehensive treatment and prevention programs. The development of clinical big data will push the health prevention industry to a new level. On the basis of such a large population base in China, the promotion of genetic testing in the general consumer market can promote the data accumulation process more quickly. Source: Singularity Network Bed Cover,Sms Bed Cover,Surgical Bed Cover,Disposable Bed Cover Xinxiang Huaxi Sanitary Materials Co., Ltd. , https://www.huaximedical.com